Breast biopsy is the process of taking samples from suspicious breast tissues and examining the taken tissues in a laboratory environment. Thus, it is examined whether the suspicious tissues in the breast contain cancer cells. Breast biopsy is the most appropriate method used today to determine whether the masses detected in the breast are cancer or not. There are different types of breast biopsy. A breast biopsy is performed to diagnose cell abnormalities that cause these conditions if a lump is detected on the breast or if some unusual changes are noticed in the breast. By means of breast biopsy, it is determined whether the patient needs a surgical operation or other treatment options, so that the patient is not exposed to unnecessary procedures.
We can list the situations that cause physicians to consider breast biopsy appropriate for the patient as follows;
Bleeding at the biopsy site: Although rare, hematoma in the form of a small bruise or hardness can be seen in the biopsy area. There is no need to intervene in the bleeding caused by the biopsy in any way, the hematoma resolves spontaneously. Bleeding requiring intervention is very rare.
Infection at the biopsy site: There is no risk of infection due to biopsy. Since the needles used for biopsy are sterile, patients do not face any infection.
Misdiagnosis: If enough tissue samples are taken from the right point during the biopsy, there is no possibility of misdiagnosis. The biopsy must be performed by an experienced physician. In addition, the examination of the tissue samples taken by expert pathologists is very important in terms of making the correct diagnosis. As a result of the biopsy, if the mass detected in the patient is determined to be benign, the patient should be checked again after 6 months and the growth of the masses should be examined.
Damage to the pleura, although rare, may occur in biopsies performed on deeply located masses under the guidance of US. This condition usually resolves spontaneously without the need for any treatment.
Change in breast appearance: This may vary depending on the size of the tissue taken from the breast and the healing process. If the tissue sample taken is large, some changes may occur in the appearance of the breast.
Additional surgical procedures: Sometimes, a complete diagnosis cannot be made as a result of the biopsy, and the physician sees the need for other examinations or finds it appropriate to perform a direct surgical operation. The reason for this situation may be due to the insufficient amount of tissue samples taken or the different opinions of the radiologist and pathology specialist. In such cases, surgical operation is mostly preferred.
Except for the cases mentioned above, if there is redness in the biopsy area, if the patient feels fever, if an unusual discharge occurs, it is absolutely necessary to consult a doctor. In these cases, which are signs of infection that require urgent treatment, drug therapy can be applied.
According to popular belief, breast biopsy is thought to cause the spread of breast cancer cells. However, this is a completely wrong assessment. The biopsy does not cause the spread of cancer cells in any way.
Before performing the biopsy, the physician should explain in detail to the patient the biopsy method he prefers, why he prefers this method, and what steps should be taken during the procedure. Thus, the patient will have a preliminary knowledge of what to expect from the procedure and his tension will be reduced to some extent. For this reason, it is extremely important that the patient is informed in detail by the physician before the biopsy. If the physician wants to change the method to be applied according to the condition of the breast abnormality, the location and other details, he should inform the patient again and explain why he has changed the method. In addition, he should inform the patient about which steps are involved in the other procedure to be applied.
The procedures applied in FNAB and cutting needle biopsy are completed in approximately 10-15 minutes. The patient can easily return to his daily work after the biopsy. Vacuum biopsy is completed in 30-40 minutes on average. After the vacuum biopsy, the patient should spend the rest of the day resting, avoid strenuous activities and not lift heavy objects. Especially after vacuum biopsy, bruising or tenderness may occur in the biopsy area. Since tenderness and bruising are a part of the healing process, no intervention is required and it completely disappears in a short time.
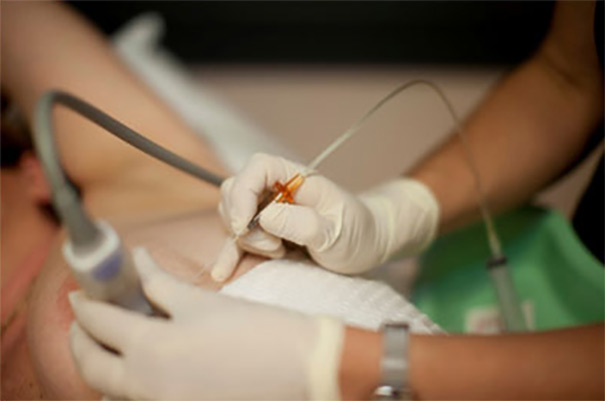
In cutting needle biopsy, called Tru-cut biopsy or thick needle biopsy, 2 – 3 mm thick needles are used. These needles collect the sample tissue through the biopsy gun.
In the cutting needle biopsy, the needle is first placed on the edge of the mass. When the button of the biopsy gun is pressed, the needle enters the mass and returns by breaking a small piece. A piece of tissue taken from the breast is placed in a solution. Then the same process is applied again and tissue samples are taken from different points of the mass to examine. The tissue pieces placed in the solution are sent to pathology for examination. A definitive diagnosis can be obtained within a few days after the tissue fragments are removed.
With the cutting needle biopsy performed by experienced people, very convenient tissue samples can be taken for diagnosis. In addition, 85-95% accurate results can be obtained. This biopsy method is extremely reliable.
Since the thickness of the needle used in cutting needle biopsy, which is the most reliable and most preferred method for diagnosing breast masses, is 3-4 mm, a few millimeters wide incision should be made on the skin. This incision heals spontaneously in a short time.
Patients may sometimes feel a slight pain after the procedure, and at the same time, there may be a slight bruising in the treated area. Although this pain and bruising is not significant, it goes away after a short time.
Cutting needle biopsy is generally described by patients as a painless and easy procedure.
This procedure can only be applied for the examination of masses that can be detected by ultrasonography.
In masses with very small dimensions, a specialist physician must perform a cutting needle biopsy in order to place the needle in the right place and to take sample tissue from exactly the right area.
Since the needle used in the cutting needle biopsy is thicker than the needles used in other biopsies, the procedure is a little more costly.
In general, it is thought that the patient should undergo a surgical operation under general anesthesia in order to make a definitive diagnosis of breast cancer among the public. However, this is a rather false belief. In most types of breast cancer, a definitive diagnosis can be made only by biopsy procedures using local anesthesia. Reliability rates of needle biopsies are quite high.
The biopsy method that should almost always be considered first in the diagnosis of breast cancer is needle biopsy (preferably cutting needle biopsy).