Meme hastalıkları ve tedavisi konusunda eğitimi olan doktorlar onkolojik ve onkoplastik meme cerrahisi uzmanlarıdır. Memenin klinik muayenesi için, genel cerrahi uzmanına, daha ideal olarak, genel cerrahlar içinden meme hastalıkları ve cerrahisi konusunda uzmanlaşmış bir onkolojik ve onkoplastik meme cerrahına gitmek en uygun olanıdır.
Meme hastalıkları, meme kanseri tedavisi ve meme cerrahisi bilgi ve deneyim gerektiren konulardır. Özel olarak meme hastalıkları ve tedavisi ile ilgilenen genel cerrahi uzmanları yani meme cerrahları memenin klinik muayenesi için seçilecek doktorlar olmalıdır.

Memede kitle fark edildiğin ilk olarak genel cerrahi uzmanından randevu alınması gerekiyor. İlk görüşmede bazı bilgiler isteniyor hastadan. Risk faktörleri değerlendiriliyor, geçmiş öyküsü alınıyor, kullandığı ilaçlar soruluyor. Ardından muayene ediliyor hasta. Muayenede meme ve koltuk altında kitle hangi bölgede, deri ile ilişkisi nasıl, deride çekintiye sebep oluyor mu? Koltuk altında lenf bezi var mı? Bunlar kontrol ediliyor. Daha sonra hastanın yaşına göre mamografi ya da ultrason tetkiki yapılıyor.
Genelde 40 yaş sonrası için mamografi öneriliyor. Mamografi düşük dozda X ışını içeren bir tetkik. Genellikle dijital mamografi tercih ediliyor. Ultrason ise mamografiye yardımcı olarak genellikle genç hastalarda yol gösterici oluyor. Hasta 35 yaş altı ise öncellikle ultrasona başvuruluyor. Ultrason X ışını değil de ses dalgası yöntemine göre çalışıyor. Kitle kist mi, içinde sıvı var mı yoksa solid mi katı mı buna bakılıyor. Sonraki aşamada ise katı içerikli kitlelere biyopsi yapılıyor. Biyopsi için birkaç yöntem var, bunlardan bir tanesi ince iğne – kalın iğne biyopsisi ve cerrahi biyopsi. Cerrahi biyopsi günümüzde çok tercih edilmiyor, daha çok kalın iğne biyopsisi yapılıyor. Kalın iğne biyopsisi nasıl yapılıyor? Bölgenin uyuşturulması sonrası otomatik bir tabancayla birkaç örnek alınıyor ve patoloji incelemesine gönderiliyor. Bu inceleme bize kitle hakkında bilgi veriyor. Eğer tümör hücresi içerisiyorsa biyopsi sonucuna ek incelemeler de yapılıyor. İmmün testler yapılıyor. Bu testlerde östrojen ve progesteron reseptörleri, her 2 düzeyi gibi bilgilere ihtiyaç oluyor. Daha sonraki aşamada hastanın evresine göre ek taramalar yapılabiliyor. Bu aşamada sıklıkla PET-CT öneriliyor. Hem sonuca kolay ulaşılıyor hem de tek tetkikte birçok organ gözlenebiliyor. PET-CT çekildikten sonra tedavi planı yapılıyor. Erken dönemdeki hastalarda daha çok cerrahi ile başlanıyor, ileri evre hastalarda ise öncelikle sistemik tedavi denilen kemoterapi ya da hormon ilaçlarıyla başlıyoruz.
Meme cerrahının veya genel cerrahi uzmanının, hastanın meme ile ilgili risklerini sorgulayarak, meme muayenesi yapmasına klinik meme muayenesi denir.
Memede kanser, 8 kadında bir görülen, görülme sıklığı kadınlarda ilk sırada olan bir kanser türüdür. Meme de kitle ise toplumda 4 kadında 1 kadında görülür.
Meme cerrahı veya genel cerrahi uzmanı klinik meme muayenesi ile hastanın meme kanseri için risk yaratan durumlarını, hormonal durumunu, aile hikayesini, hastalıklarını, doğurganlığını, emzirme veya vücut kitle indeksi (BMI) gibi kişisel durumlarını, meme sağlığını etkileyebilecek ilaçlarını ve alışkanlıklarını, meme ile ilgili daha önce geçirdiği hastalıkları, ameliyat veya biyopsileri sorgulayarak memeyi muayene eder.
Tüm bu sorgulamalardan elde ettiği verileri, hastanın elle yapılan muayenesi ile birleştirir. Hastanın elde olan verilerine uygun görüntüleme yöntemi veya yöntemlerinin önerir. Bu görüntüleme sonucunda elde edilen verileri, klinikte elde ettiği muayene ve sorgulama verileriyle birleştirir.
Gerekiyorsa daha ileri ek görüntülemeler ve tetkikler ister. Sonuçta meme cerrahı veya genel cerrahi uzmanı, her hasta için bir meme kanseri risk değerlendirmesi ile hastaya özel kişiselleştirilmiş izlem önerir.

Meme muayenesi, öncelikli olarak meme hastalıkları ve meme kanseri konusunda risk yaratacak durumlara neden olacak konuları sorgulayarak başlamalıdır.
Klinik meme muayenesine, hastanın memesindeki yakınması ile ilgili durumları etkileyecek tüm olasılıklar sorgulanarak başlanır.
Meme hastalıkları konusunda yakınması olan hastada, geçirdiği ameliyatlar, aile hikayesi, hormonal düzeni, kullandığı ilaçlar, mesleği, alışkanlıkları, evlilik ve doğum durumu, emzirme, genetik yatkınlığı, beraberinde olan hastalıkları ve kullandığı veya geçirdiği tedaviler ayrıntılı olarak sorgulanır.
Hastanın bu durumla ilgili var olan geçmiş zamana ait tüm tetkikleri değerlendirilir. Sonra meme cerrahı veya genel cerrahi uzmanı memede ağrı, memede kitle, memede enfeksiyon, memede kist ve benzeri yakınması olan kişiyi elle muayene eder. Bu elle meme muayenesi, memenin kapladığı tüm alanı, memedeki yakınmalara neden olacak yansıması olacak alanları, olası meme kanserinin yayılabileceği / sıçrayabileceği tüm alanları ve lenf bezlerinin klinik elle muayenesini içerir.
Elle meme muayenesinden elde edilen tüm bulgular ve özellikleri kaydedilir. Hastanın sorgulamasından elde edilen verilerle birleştirilerek değerlendirilir.
Meme konusunda yakınması olan hasta için, yakınmasına ve yaşına en uygun görüntüleme ve gerekli kan tetkikleri istenir. Daha sonra meme cerrahı bu meme görüntüleme ve kan tetkiki sonuçlarını hastanın klinik meme muayenesi ve yakınmalarına göre yorumlar.
Elde edilen sonuca göre ya daha ileri tetkiklere geçilir. Ya da saptanan duruma uygun tedavi veya meme hastalığının izlemi önerilir. Belirlenen izlem aralığına göre hastanın, meme klinik muayenesinden elde edilen bulguların zaman içinde değişiklik gösterip göstermediği, ilerleyip ilerlemediği, bir tedavi önerildi ise tedaviye yanıtı değerlendirilir. Bu meme izlemlerinde hastaya uygun radyolojik meme görüntüleme yöntemleri de tekrar edilebilir ve önceki değerlendirmelerle karşılaştırılır.

Silicone breast prostheses were created in 1963, inspired by the plastic bags used in blood transfusions that resemble a breast when carried. Silicone prostheses are materials filled with gel-like silicone, surrounded by a more solid silicone sheath, and can be produced in a round or oval shape. The consistency of the gel is very similar to that of an adult female breast and they are not noticeable on the body.
Silicon is one of the most common elements on earth. The combination of silicon with other elements creates a family of silicons with different structures. Depending on the properties of the joint, silicones can be found in solid, gel or liquid form (Figure 1). The most important difference between silicones used in industry and daily life and those used in breast prostheses is that medical silicones are pure and compatible with the body. Apart from breast prostheses, medical silicones are widely used in areas ranging from catheters to joint prostheses, heart valves and penile prostheses.
Figure 1. As the chains around the silicones lengthen and bond together, their consistency hardens
There are also silicone breast prostheses filled with water, not silicone gel. However, an implant filled with water is not preferred because it is harder in consistency. There is also the possibility of leakage and leakage in water-filled prostheses.
Types of Silicone Prostheses
Types of Implants by Shape:
Silicone prostheses are produced in drops and round forms. Drop prostheses are also called anatomical prostheses because their downward-expanding structure resembles the side view of the breast when viewed from the side (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Anatomical prostheses (top) and round prostheses (bottom)
Types of Implants According to the Consistency of the Gel It Contains:
Silicone prostheses are also divided into two according to the consistency of the gel they contain: soft gel and cohesive gel prostheses that keep their shape. Although soft gel implants are more suitable for the natural consistency of the breast, they are slightly displaced by gravity in their sheath. Cohesive gels, on the other hand, maintain their shape in any case and can not only enlarge the breast in volume, but also shape it into a certain shape. However, the breasts on which these prostheses are placed feel harder to the hand. In the last few years, slightly softer versions of Cohesive silicones have also been introduced as an option (Allergan® SoftTouch, etc.).
Most gel-containing dentures today use a form of gel that does not flow out when burst or cut (Fig. 2). This feature is a precaution to reduce the problems in leakages that may occur due to wear or accident.
Figure 2. An implant containing a cohesive gel does not flow out when burst or cut
If an implant containing a cohesive gel is used, the shape of the chosen silicone prosthesis will affect the shape of the enlarged breast. Which prosthesis to choose depends on what kind of breast shape you like. In general, women’s preferences about breasts can be divided into two (Figure 3):
● Rounded breasts that fill the décolleté and look like they’ve been pushed up with a bra
● Drop-shaped breasts that come with a flat slope down the décolleté and take a round form after the nipple
Figure 3. Which breast shape do you like more? It can be thought that those who prefer the two breast silhouettes on the left like drops, those who prefer the two silhouettes on the left like the round breast shape.
Although it is not a general rule, anatomical prostheses are preferred to achieve the drop shape, and round prostheses are preferred to achieve the round shape.
Other reasons for choosing anatomical prostheses are:
● In very thin patients with no breasts, a cohesive and rounded prosthesis can create a sudden and unnatural transition in the upper part. In such patients, using submuscular and anatomical prosthesis is a better option.
● In patients with slightly drooping nipples, the need for breast augmentation surgery can be reduced by using an anatomical prosthesis to raise the nipple.
The situations in which round prostheses are preferred are as follows:
● Patients who do intense sports such as tennis and swimming and who will be implanted under the muscle: If an anatomical prosthesis is used in these patients, the possibility of the prosthesis turning outward with muscle movements may create asymmetry. Even if round prostheses rotate, this may not produce a noticeable result.
● To fill the gap in the upper part of patients who will be augmented with breast augmentation.
The latest development in silicone technology is the implants containing gel in two different consistencies in the same sheath. Aiming for a more natural look, this technology is available in Polytech 4inTwo Series and Allergan’s 510 series. The part of the drop prosthesis that rests on the chest wall contains a softer silicone and the part under the nipple contains a harder silicone (Figure 4). Thus, the transition line created by the top part of the silicone, especially in the side profile, is eliminated and the projection of the nipple is increased.
Figure 4. Polytech® 4inTwo prostheses with two different densities of silicone
Implant Types According to Sheath Properties:
While the surface of the silicone sheath was flat and smooth in the first periods, textured forms were adopted later on (Figure 5). The sleeves of silicones are also technologically advanced and have become more sealed by adding several layers. The purpose of these changes is to reduce the event called capsular contracture. One of the rough forms is polyurethane coated prostheses. Once the silicone enters the body, this coating begins to melt and thus creates an intermediate zone that will reduce the formation of capsular contracture. It is especially preferred in patients who develop capsule contracture and whose prosthesis will be replaced.
Figure 5. Silicone prostheses with different sheath properties: Top left – formerly flat-surfaced transparent prostheses; Top right – polyurethane coated prosthesis; Bottom row – dentures with rough surface
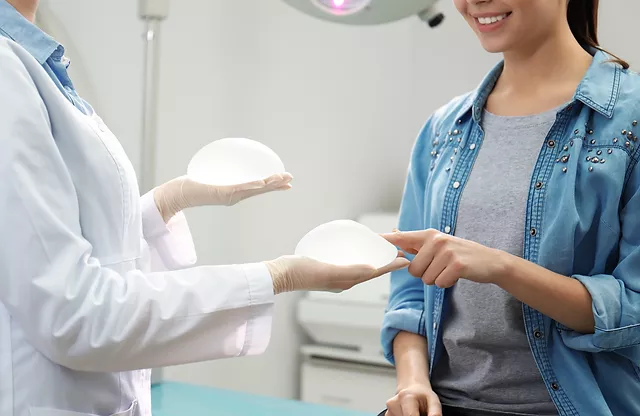
Every woman’s breast is as unique as her fingerprint. The structure of the rib cage, its angle, the thickness and flexibility of the skin, the posture, the shape and width of the area where the mammary gland begins (footprint) are different in every woman and lead to the development of a personalized breast structure. The silicone prostheses produced, on the other hand, come in certain molds because they are fabricated. A manufacturer’s silicone variety is between 250-300. The most important step of breast augmentation surgery is to choose the most suitable prosthesis among them.
How to choose the most suitable prosthesis for you? In this regard, the first step is to decide what size you want. Psychological studies show that women do not dare to express the dimension they actually want. Another mistake made in this regard, especially in Turkish patients, is to confuse the size of the bra, such as 80-90, with breast size. The best expression of breast size is the “cup sizes” that go as A, B, C, D DD.
The next step is to choose the breast shape. You can do this by bringing photos of the breasts you like. At this stage, it becomes somewhat clear whether a round or drop-shaped prosthesis will be chosen.
Of course, you will also need to have a chest structure in which what you want can be applied. For this, your doctor takes detailed measurements of your breasts. These are listed as width, height, projection, amount of stretching, distance between neck and nipple, skin thickness, etc. The most critical of these measurements is the width of the breast. The limiting step in determining the size of the prosthesis is the width of the breast base. Because if you go sideways, more armpits will be entered, so it cannot be exceeded.
Then, your doctor chooses a few prostheses that are most suitable for you from the catalogs of companies that produce various silicone prostheses according to the measurements they take. There are two methods to pre-determine which of these will yield results: Your pre-operative photographs can be uploaded to the simulation system, and how the results will be obtained with the selected prostheses can be simulated. Crisalix® is one of these systems. By looking at this simulation, a sketch is formed that you can discuss with your doctor about what size or shape you want in general, although it is not exactly one-to-one. But the real live trial is done by placing the prostheses selected during the surgery on your chest and watching how you sit at the table while you sleep. Usually, several types of prostheses and trial pairs are brought in sizes close to the measurements made for the surgery.